Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower vs. Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny
Comparison and Differences
Differences between Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower and Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny
If you are looking for a more modern desktop, then you should go with the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower which was released in 2015. The Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny is older and entered production in 2013.
If you are looking for the smaller form factor the Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny is the right one for you. It is smaller than the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower and will fit more easily under your desk.
Processor
Usually the newer the generation of the CPU, the better the performance and efficiency is. If your budget allows it, you should go with the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower as it is running a newer generation CPU. This is not to say that Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny is bad - it can still run some powerful CPUs, albeit being an older generation.
Memory
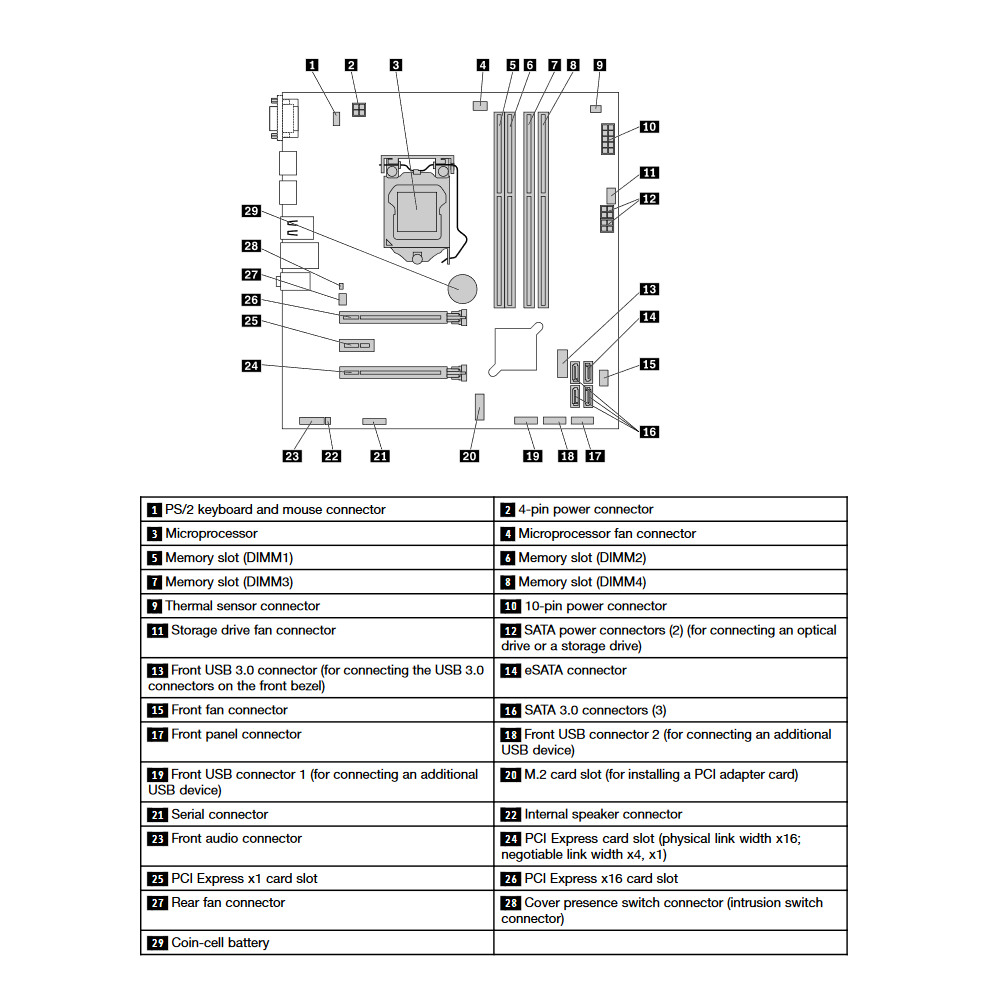
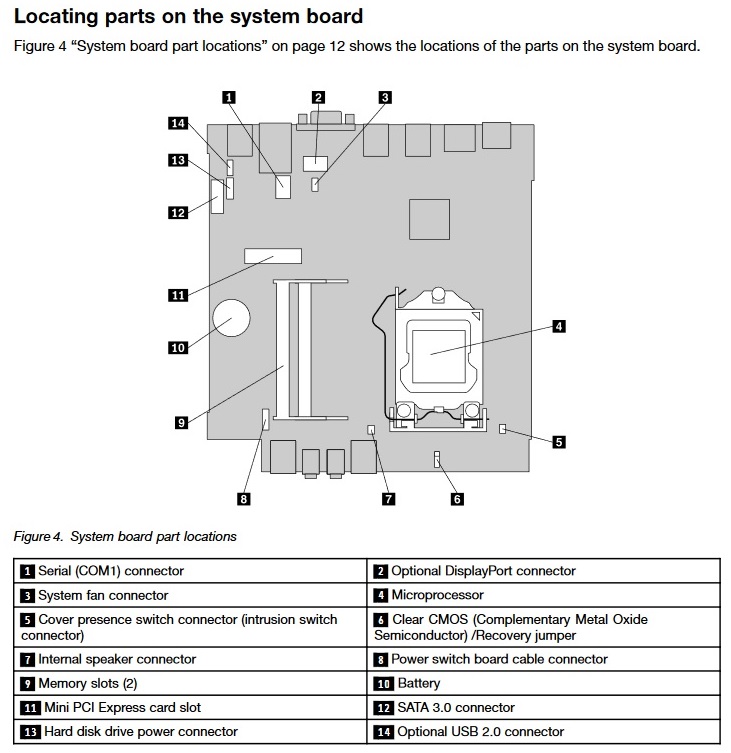
The Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower has 4 RAM slots while the Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny has only 2 slot(s). This is not something to worry about. Just make sure you take it into consideration when planning how much RAM you are going to use.
The Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower is using the faster 2133 MT/s RAM. The Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny is slower by supporting RAM speeds of up to 1600 MT/s. Additionally, if you will be needing a lot of RAM, better go for the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower as it has the ability to run 64 GB of RAM. The Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny can do a bit less at max 32 GB. Most of the times, this should be sufficient for the majority of users.
Ports
In total the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower has 8 USB ports. The Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny is inferior in this regard and packs 5 USB ports. In any case, if you miss USB ports, you can always purchase a USB hub. None of the desktop models has a USB 3.1 port (10Gb/s), so if you need a fast connection to your peripherals, like external Solid State Drive, you will need to look elsewhere.
DisplayPort is crucial for any desktop machine. It is good to see that both models are featuring DisplayPorts. However, the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower comes with 2 ports, while the Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny has only 1. If you are planning to use multiple monitors, the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower is the better choice.
None of the models has an HDMI port. If your monitor supports only the HDMI interface, you will need to buy an adapter. Such adapters are cheap so nothing to worry about.
SATA ports are placed on the system board and it is where you connect your HDD, SSD and Optical Disk Drives. More SATA slots will allow you to have more drives running at the same time. In this regard the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower is better equipped as it comes with 3 SATA slot(s), while the Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny has 1 slot(s).
M.2 SSD interface allows you to transfer data with higher speeds compared to the old SATA interface. Unfortunately, neither the Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny, nor the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower has one. However, you can still use a SATA SSD drive which should give you satisfactory performance.
Make sure that the available M.2 slot supports the PCIe (also called NVMe) interface. This is important as there are M.2 slots which support only the inferior SATA III interface. For comparison, the SATA III interface has max speeds of 6Gb/s, while the PCIe 3.0 x4 will support speeds up to 32Gb/s!
Power Supply
Having a Power Supply Unit with high power rating is important, if you are going to use components which require extra power. The Lenovo ThinkCentre M83 Tiny comes with a decent 65 Watt PSU, but the Lenovo ThinkCentre M800 Tower has a more powerful one rated at 250 Watts. Choosing either one depends on your specific requirements and use case. Also don't forget that some models might have more than one PSU option - try to always get the most powerful one, especially if you plan to upgrade to a powerful GPU.