How to Identifying Your Graphics Card
In the ever-evolving landscape of PC hardware, the graphics processing unit (GPU) stands as a cornerstone of system performance, particularly for gaming and content creation. However, many users find themselves at a loss when it comes to identifying the exact model residing in their machine.
We’ll begin with the most straightforward method, leveraging built-in operating system tools that require no third-party software. Subsequently, we’ll explore a more in-depth approach using GPU-Z, a lightweight yet powerful utility favored by enthusiasts for its comprehensive hardware reporting capabilities.
While physical inspection of the GPU itself can sometimes yield results, this method is not always reliable. Many graphics cards only display generic branding such as “GeForce RTX” or “Radeon RX” on their shrouds, omitting specific model information.
The Importance of GPU Identification
Understanding the specific GPU model in your system is crucial for several reasons:
- Performance Expectations: Your GPU largely determines your system’s capabilities in gaming and GPU-accelerated applications.
- Driver Updates: Knowing your exact model ensures you download the correct drivers, critical for optimal performance and stability.
- Compatibility: Certain software and games have specific GPU requirements or optimizations.
- Thermal Characteristics: Different GPUs have varying thermal profiles, influencing cooling requirements and expected operating temperatures.
- Power Consumption: GPU models vary significantly in their power draw, impacting PSU requirements and system efficiency.
- Feature Set: Modern GPUs support various technologies (e.g., ray tracing, DLSS) that may not be available on older or lower-tier models.
- Upgrade Planning: Accurate knowledge of your current GPU aids in making informed decisions about potential upgrades.
Identifying Your GPU Through Windows
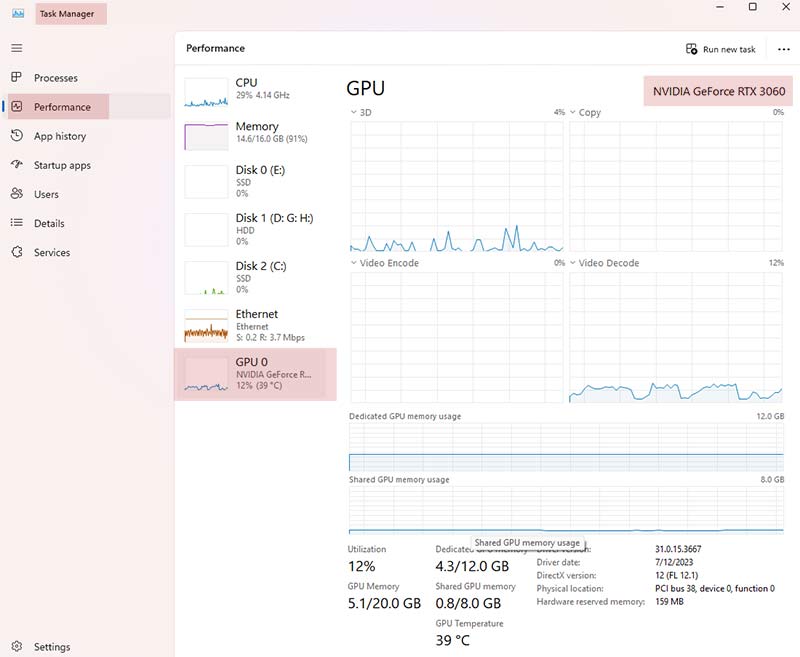
Screenshot of Windows 11 Task Manager with information about the GPU
The simplest method to identify your GPU uses built-in Windows tools:
- Press the Windows key and type “Task Manager.”
- Open Task Manager and navigate to the “Performance” tab.
- Select “GPU” from the left-hand menu.
This view provides essential information, including:
- GPU Model Name
- Dedicated GPU Memory
- Driver Version
- DirectX Support Level
- Current GPU Temperature and Utilization
While this method is quick and accessible, however it offers limited details compared to specialized tools.
A more detailed GPU information
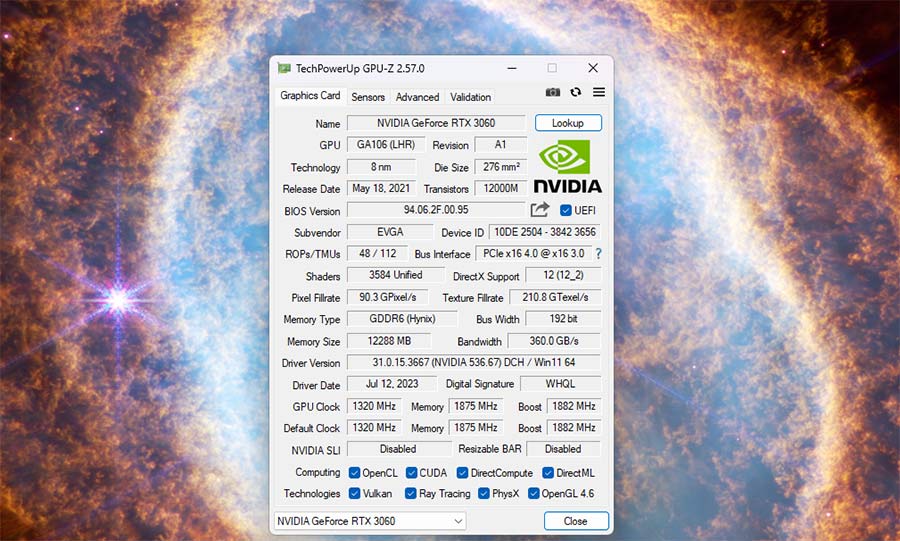
For a more thorough examination of your GPU’s capabilities, we recommend GPU-Z. This free, lightweight application provides an extensive array of information, including:
- GPU Architecture and Manufacturing Process
- Release Date
- Core Configuration (Shaders, TMUs, ROPs)
- Memory Specifications (Size, Type, Bus Width, Bandwidth)
- Clock Speeds (Base, Boost, Memory)
- Ray Tracing Capabilities
- PCIe Interface Version
GPU-Z also supports systems with multiple GPUs, allowing you to switch between integrated and discrete graphics solutions for comprehensive analysis.
Downloading and and using GPU-Z
- Download GPU-Z exclusively from the official TechPowerUp website to ensure a malware-free installation.
- Install the application – the process is swift due to its small footprint.
- Launch GPU-Z to immediately view your GPU’s specifications.
The application auto-updates and includes a built-in stress test for verifying PCIe configuration and stability.
Linux and macOS Users
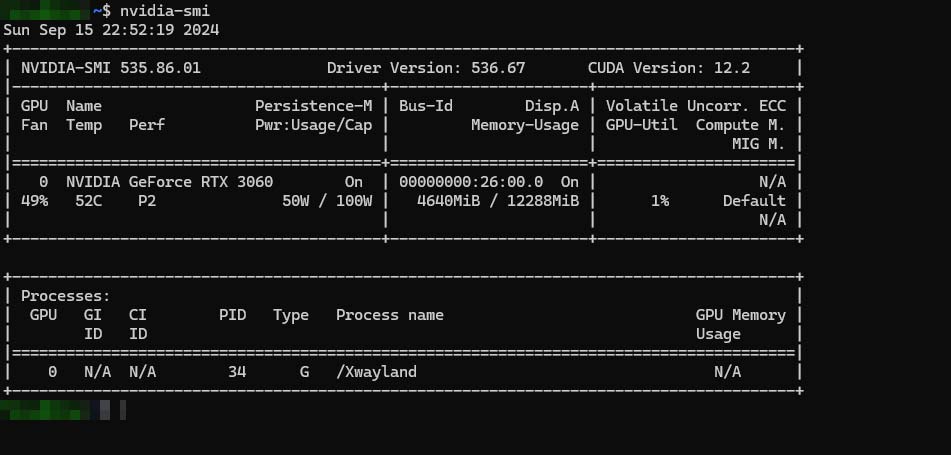
Linux users can identify their GPU through terminal commands such as lspci, lshw -C display or nvidia-smi if you have NVIDIA GPU. For a GUI-based solution, applications like Hardinfo provide comprehensive hardware information.
macOS users can find basic GPU information under “About This Mac.” For Apple Silicon Macs, more detailed GPU specifications are available in the “Graphics/Displays” section of the System Report. Third-party applications like AIDA64 offer additional insights for those seeking more granular information.
In conclusion, whether you’re troubleshooting performance issues, planning an upgrade, or simply satisfying your curiosity, knowing your GPU model is an essential piece of the PC hardware puzzle. With the methods outlined above, you’re now equipped to uncover this crucial information, regardless of your technical expertise or operating system preference.